Introduction
Vegan Vitamin D is important for strong bones, a healthy immune system, and mood stabilization. However, vegans have a much harder time meeting their vitamin D requirements through plants. That said, there are many vegan choices available. As you will see in this guide, the best sources and practical methods to help vegans ensure they maintain high vitamin D levels.
Why Is Vegan Vitamin D Important?
Vitamin D helps your body absorb calcium, critical for your bones and teeth, strengthens immunity, and lowers the risk of chronic diseases. Symptoms of deficiency include fatigue, bone pain, and depression. For vegans, who may not have as many natural sources of this vital nutrient, vegan vitamin d is especially important to ensure adequate intake.
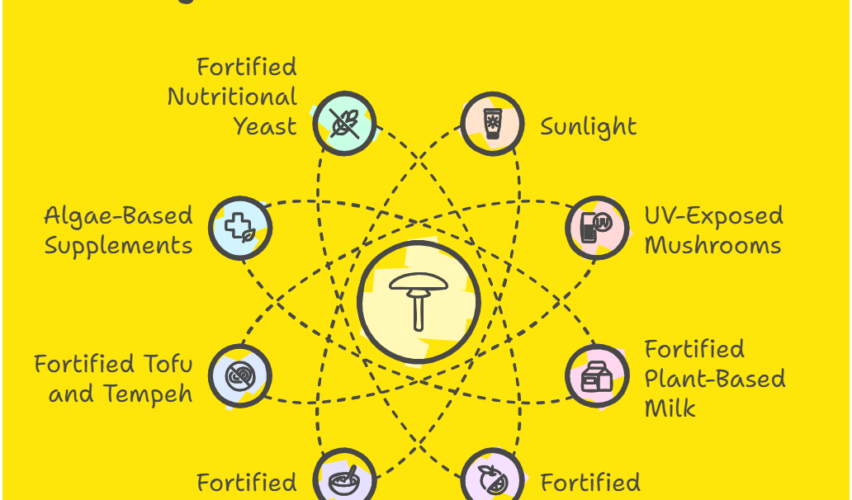
10 Best Vegan Sources of Vitamin D
1. Sunlight (Natural Source)
Vitamin D is made by the body when the skin is exposed to sunlight. Just 15-30 minutes of sun on your arms and face a few times a week can help. However, sunlight alone may not be enough, especially in winter or cloudy climates.
2. UV-Exposed Mushrooms
Mushrooms like maitake, portobello, and shiitake produce vitamin D2 when exposed to UV light. Cook them in stir-fries, soups, or salads to add this natural source to your meals.
3. Fortified Plant-Based Milk

Soy, almond, and oat milk are often fortified with vitamin D2 or D3. Add them to smoothies, cereal, or coffee. Many varieties also contain calcium, providing double the bone health benefits.
4. Fortified Orange Juice
A glass of fortified orange juice is a simple, refreshing source of vitamin D. Check labels to ensure it’s vegan and fortified with plant-based D2 or D3.
5. Fortified Cereals
Several breakfast cereals are fortified with vitamin D, making them a convenient option. Pairing them with fortified plant-based milk can boost your intake.
6. Fortified Tofu and Tempeh

These protein-rich staples are sometimes fortified with vitamin D. Add them to stir-fries, scrambles, or salads for a nutritious meal.
7. Algae-Based Vitamin D Supplements
Algae-based D3 is a reliable vegan supplement, especially during winter or for those with limited sun exposure. Look for third-party-tested brands to ensure quality.
8. Fortified Nutritional Yeast
Nutritional yeast, often enriched with D3, adds a savory, cheese-like flavor to dishes. Sprinkle it on pasta, popcorn, or roasted vegetables.
9. Fortified Vegan Yogurt
Many plant-based yogurts, such as those made from soy or coconut, are fortified with vitamin D. Enjoy them with fruit, granola, or as a snack.
10. Chanterelle Mushrooms
Chanterelle mushrooms are rich in vitamin D2 and can add a unique flavor to stews, risotto, or pasta.
Additional Tips to Boost Vitamin D Absorption
- Pair with Healthy Fats: Vitamin D is fat-soluble, so eat it with healthy fats like nuts, seeds, or avocado.
- Spend Time Outdoors: Regular sun exposure is beneficial, especially in the morning.
- Consider Seasonal Supplements: A vegan D3 supplement can be helpful during winter months.
Symptoms of vegan vitamin d Deficiency
Look out for signs such as:
- Fatigue or low-energy
- Bone or muscle pain
- Mood changes, including depression
Final Thoughts
Vegans can maintain healthy vitamin D levels through a combination of natural sunlight, fortified foods, and supplements. Incorporating these sources into your diet will support your bones, immune system, and overall health. A balanced diet with proper vegan vitamin D intake ensures a healthy, vibrant lifestyle. al health, consider incorporating both into your regimen, ensuring your body receives the support it needs to thrive.




[…] Click this related article… […]